Types of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural Diffusion
The definition of cultural diffusion (noun) is the geographical and social spread of the different aspects of one more cultures to different ethnicities, religions, nationalities, regions, etc. Cultural diffusion is about the spreading of culture over time. There are many types of cultural diffusion, and in this guide we will go over the types and provide examples. The following study guides in this unit series go into additional examples of cultural diffusion in specific historic and modern contexts.
Relocation Diffusion
Relocation Diffusion occurs when people move from their original location to another and bring their innovations with them. Immigration from country to country, city to city, etc. As they relocate to a new location, they bring their ideas, cultural tradition such as food, music, and more. As masses of individuals immigrate to a new environment, they bring along their cultural connections, influencing others in the new environments. Relocation diffusion can also be forced rather than chosen.
Examples
Many cultural components of Southern US architecture, cuisine, and music have African and Caribbean origins due to the forced relocation and enslavement of African people during the trans-atlantic slave trade.
Another example is the cultural diffusion from when over two million persecuted Jewish people fled Eastern Europe between 1881 and 1914 to live in Britain or the United States.
Expansion Diffusion
Expansion Diffusion is the spread of an idea through a population where the amount of those influenced grows continuously larger. There are three sub-types of Expansion diffusion: Stimulus, Hierarchical, and Contagious.
Contagious Diffusion
Contagious Diffusion is defined as distance-controlled spreading of an idea through a local population by contact from person to person. Similarly to a disease, it spreads rapidly from one source to others from person to person. Another way to think of it is like the spreading of a forest fire.
Examples of contagious diffusion
religions when people are in contact with belief systems especially universalizing religions such as Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam. Missionaries spread christianity.
the globalization of social networking, media platforms.
when videos or songs go viral, they contagiously diffuse like wildfire through the help of modern technological innovations. All memes exhibit contagious diffusion!
Hierarchical Diffusion
Hierarchical Diffusion is when an idea spreads by passing first among the most connected individuals, then spreading to other individuals. Think of the chain of command in businesses, and the government. There’s somewhat of a hierarchy in terms of position of authority.
Examples of hierarchical diffusion
The Federal government such as the president, vice president, cabinet members are the first to be informed of governmental matters before the general public and state government employees.
A business CEO is more informed on matters within their company before the spread of that information to employees and the general public.
You can also think about popular music first reaching urban centers, city communities in New York, LA, Chicago before gaining popularity among the wider public.
Stimulus Diffusion
Stimulus Diffusion is when an idea diffuses from its cultural hearth outward, but the original idea is changed by the new adopters. Almost all cultural diffusions will have some aspect of stimulus diffusion because of the ways culture adapts to new environmental, social, and political conditions.
Examples of stimulus diffusion
The McDonalds fast food chain originating in the US midwest having developed different menu items in different regions of the world.
The changing interpretations of religious texts as they are translated into other languages.
Maladaptive Diffusion
Maladaptive Diffusion is the adoption of diffusing traits that are not practical or reflective of a region's environment or culture.
Examples of maladaptive diffusion:
the spread of grass lawns and monoculture crops which are both actively very harmful to the environment
the popularity of wearing blue jeans in any weather despite the impracticality of wearing them in the winter season
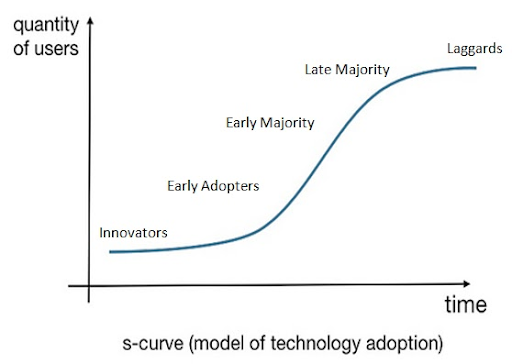
This image depicts the Diffusion S Curve by Hagerstrand specifically in the model of the adoption of technology. The stages include innovators, early adopters (small groups of those that can afford), followed by majority adopters (faster rate of adoption once price decreases) and lastly laggards/late adopters (rate of adoption slows down). The trend resembles the letter S therefore is called an S curve.